跨尺度的冻土水动力数值模拟研究——分子尺度下多孔介质中水的冻融过程
Subject:跨尺度的冻土水动力数值模拟研究——分子尺度下多孔介质中水的冻融过程
Abstract:
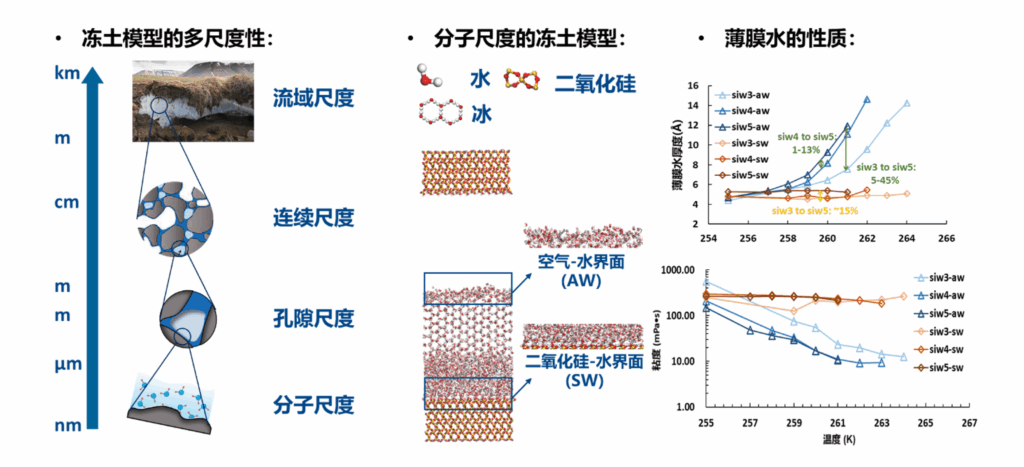
全球气候变化的背景下,冻土退化显著影响水文过程,重塑水文地质,改变产汇流机制。冻土数值模型具有多尺度性:宏观尺度适用于解决实际冻土问题,其表现依赖于对土壤中水冻结-融解过程机制的理解;微观尺度的模型则为宏观模型提供理论支持。通过分子动力学(MD)模拟,构建了分子尺度的冻土模型,探究了微观尺度下冻土中孔隙水的相变以及界面过程,量化了不同界面处薄膜水的性质。研究发现,饱和及非饱和冻土体系中水相变的驱动力不同,非饱和体系中不同界面上薄膜水的对温度响应也不同。这表明,薄膜水(即界面过程)在水的相变以及流动中起着重要作用。这些看似矛盾的结果突显了用宏观概念定义被限制在纳米级孔隙中的物质相态的困难,也为传统水文模型的物理模型的改进提供建议。
Reference:
Ji, S., Wu, P., Chen, L., Yang, Y., Pi, X., McKenzie, J. M., & Liang, X*. (2025). Quantifying permafrost thawing and its impact on lake storage dynamics in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Hydrology, 650, 132529. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2024.132529.
Ji, S., Yang, Z., Lei, L., Galindo Torres, S. A.*, & Li, L*. (2024). Estimation of the ice melting point in molecular dynamics simulations based on the finite-size effects. Physical Review E, 109(1), 14108. http://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.109.014108.
Ji, S., Torres, S. A. G., Chen, J., Lei, L.*, & Li, L*. (2025). Molecular dynamics simulation of film water thickness and properties at different interfaces in partially saturated frozen soil systems. Scientific Reports, 15(1), 2343. http://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-85975-3.

